TYPES OF CYBER ATTACKS
Business Email Compromise :
Business email compromise (BEC)—also known as email account compromise (EAC)—is one of the most financially damaging online crimes. It exploits the fact that so many of us rely on email to conduct business—both personal and professional.
In a BEC scam, criminals send an email message that appears to come from a known source making a legitimate request, like in these examples:
- A vendor your company regularly deals with sends an invoice with an updated mailing address.
- A company CEO asks her assistant to purchase dozens of gift cards to send out as employee rewards. She asks for the serial numbers so she can email them out right away.
- A homebuyer receives a message from his title company with instructions on how to wire his down payment.
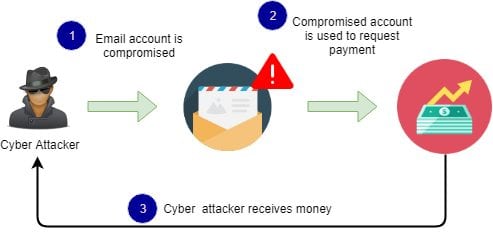
A BEC attack is where the attacker targets specific individuals, usually an employee who has the ability to authorize financial transactions, in order to trick them into transferring money into an account controlled by the attacker.
BEC attacks usually involve planning and research in order to be effective. For example, any information about the target organization’s executives, employees, customers, business partners and potential business partners, will help the attacker convince the employee into handing over the funds.
BEC attacks are one of the most financially damaging forms of cyber-attack.
How Business Email Compromise Works :
How to avoid Business Email Compromise :
- Be careful with what information you share online or on social media. By openly sharing things like pet names, schools you attended, links to family members, and your birthday, you can give a scammer all the information they need to guess your password or answer your security questions.
- Don’t click on anything in an unsolicited email or text message asking you to update or verify account information. Look up the company’s phone number on your own (don’t use the one a potential scammer is providing), and call the company to ask if the request is legitimate.
- Carefully examine the email address, URL, and spelling used in any correspondence. Scammers use slight differences to trick your eye and gain your trust.
- Be careful what you download. Never open an email attachment from someone you don't know, and be wary of email attachments forwarded to you.
- Set up two-factor (or multi-factor) authentication on any account that allows it, and never disable it.
- Verify payment and purchase requests in person if possible or by calling the person to make sure it is legitimate. You should verify any change in account number or payment procedures with the person making the request.
- Be especially wary if the requestor is pressing you to act quickly.
TYPES OF CYBER ATTACKS
- Man In The Middle Attack
- Brute Force & Dictionary Attack
- SQL Injection
- Botnet
- Trojan Horse
- Malware Attack
- Cryptojacking
- Phishing
- Session Hijacking
- DNS Spoofing
- DOS Attack
- Business Email Compromise
- Drive-by Attack
Did you like our works?
We are known for Website Development and Website Designing, along with Android iOS application development in Mumbai, India.
